Andhra Pradesh is a state in southeastern India with a rich cultural and historical legacy. Here’s a summary based on your detailed information:
Andhra Pradesh Geography
- Location: Southeastern India, bordered by Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Telangana, and Odisha, with a coastline along the Bay of Bengal.
- Physiographic Regions:
- Coastal Plain: Fertile alluvial soil, watered by rivers like the Godavari and Krishna.
- Eastern Ghats: A mountain range running parallel to the coast with porous soils.
- Plateau Region (Rayalaseema): Composed of gneissic rock with elevations exceeding 2,000 feet, marked by red sandy soil and isolated hills.
Andhra Pradesh Climate
- Seasons:
- Summer: March to June, with temperatures often exceeding 95°F (35°C).
- Monsoon: July to September, bringing heavy rains.
- Winter: October to February, cooler temperatures ranging from 60°F to 95°F (15°C to 35°C).
Andhra Pradesh Natural Resources and Industry
- Agriculture: Major producer of rice and tobacco, with significant cultivation of other cereals, pulses, and vegetables. Rivers support irrigation and agro-industries.
- Forestry and Fishing: Timber production, non-timber forest products, and a significant fishing industry, including prawns and shrimp.
- Mineral Resources: Asbestos, mica, manganese, barite, coal, natural gas, and historical diamond mines.
- Manufacturing: Industrial growth in shipbuilding, aeronautics, chemicals, textiles, and steel.
Andhra Pradesh People and Culture
- Population: Diverse, with Telugu as the main language and significant communities of Urdu speakers and Scheduled Tribes and Castes.
- Religion: Predominantly Hindu, with smaller Muslim and Christian communities.
- Cultural Contributions: Rich in classical music (Karnatak), dance (Kuchipudi), and literature. Telugu is a prestigious literary language.
Andhra Pradesh History
- Ancient Times: References to Andhras in Sanskrit texts, the Satavahana dynasty’s trade with Rome, and the flourishing of Buddhism.
- Medieval Period: Chalukyas and Kakatiyas influenced the region, with significant advancements in culture and military power.
- Colonial Era: The British gained control of Andhra areas from the nizam and the French. The Telugu-speaking regions were incorporated into separate administrative divisions.
- Post-Independence: The formation of Andhra Pradesh in 1956, the separation of Telangana in 2014, and ongoing political dynamics with significant leaders like Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao and Nara Chandrababu Naidu.
Andhra Pradesh Governance
- Structure: A governor appointed by the President of India, with real power held by a Chief Minister and a unicameral Legislative Assembly.
- Capital: Amaravati (since 2024), following Hyderabad’s role as the joint capital with Telangana until 2024.

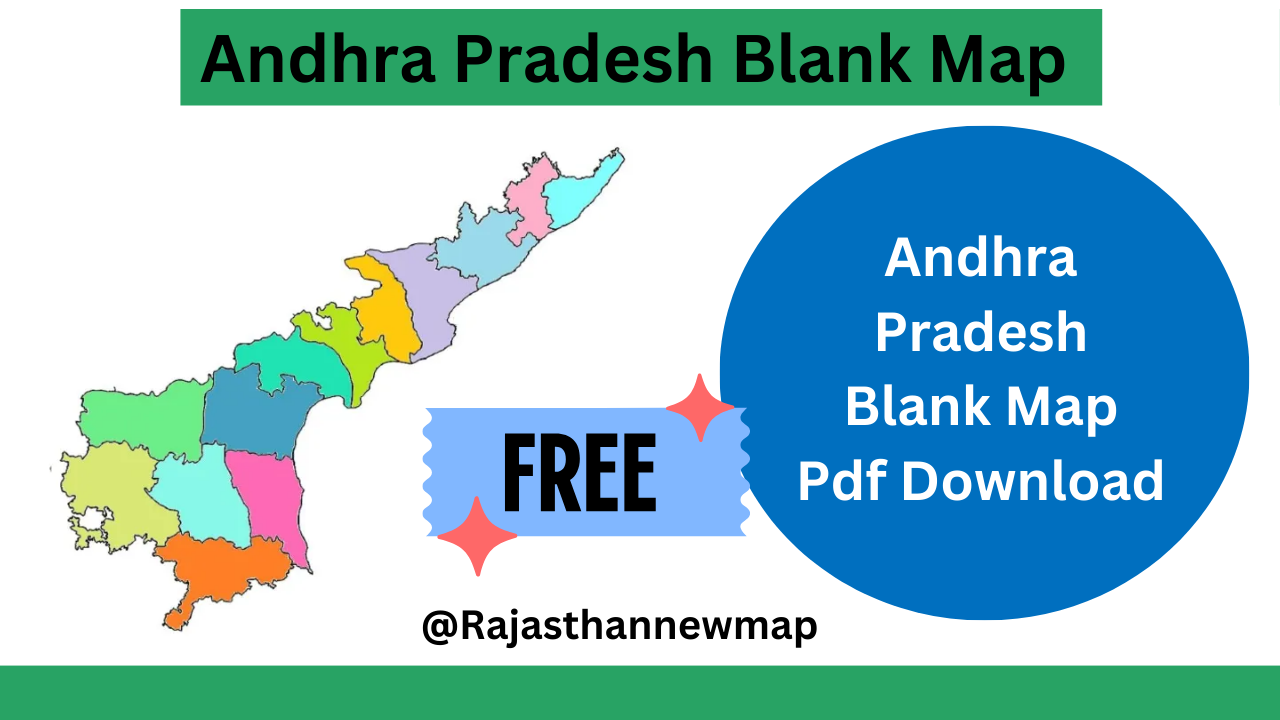
As of 2024, Andhra Pradesh is divided into 26 districts. Here’s a list of the districts:
Alluri Sitharama Raju – Anakapalli – Anantapur – Annamayya – Bapatla – Chittoor – East Godavari – Eluru – Guntur – Kakinada – Konaseema – Krishna – Kurnool – NTR – Nandyal – Palnadu – Parvathipuram Manyam – Prakasam – Sri Potti Sriramulu Nellore – Sri Sathya Sai – Srikakulam – Tirupati – Visakhapatnam – Vizianagaram – West Godavari – YSR
Andhra Pradesh Blank Map Pdf Download